What Is an Extruder Machine
Understanding what an extruder is is of paramount importance for professionals in the industrial material processing and manufacturing sectors. As core equipment for the continuous molding of materials such as plastics and rubber, it serves as a critical backbone for numerous production lines. This article will address your key questions by covering the basic fundamentals, operating principles, key components, classification methods, application scenarios, and global market demand and trends of extruders.

Basic Overview of Extruders
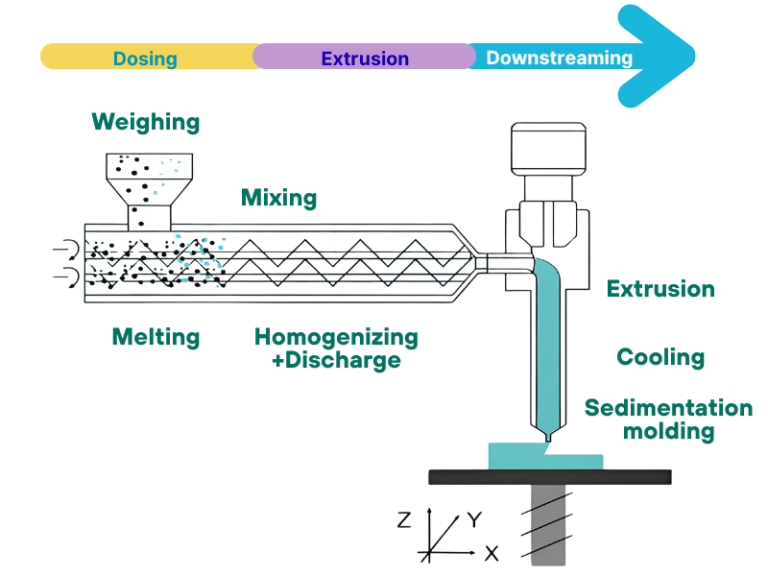
An extruder is a type of mechanical equipment that processes raw materials such as plastic pellets, rubber, or composite materials through heating, melting, mixing, and extrusion processes. It shapes these materials into continuous profiles, sheets, pipes, or films. Its core value lies in the ability to achieve efficient, stable, and customizable material molding, making it an indispensable piece of equipment in large-scale production scenarios.
Operating Principles of Extruders
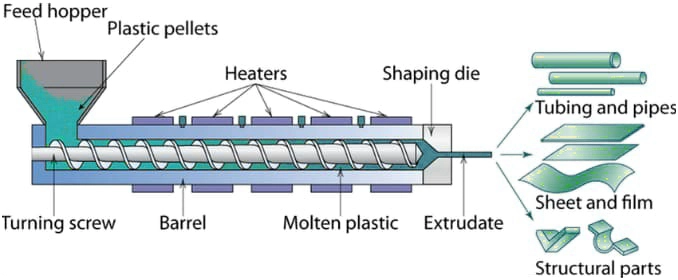
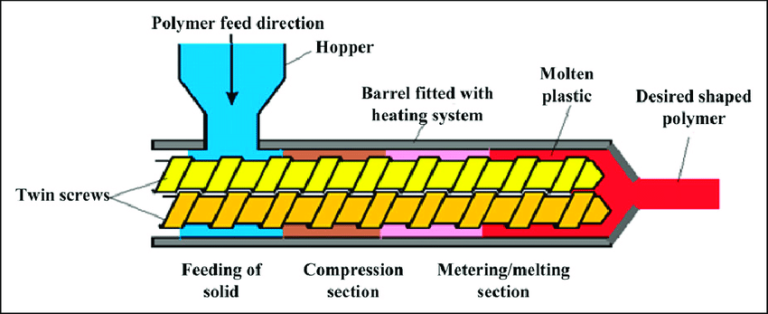
1.Feeding Stage: Raw materials such as plastic pellets or rubber enter the equipment through a hopper and are steadily conveyed into the barrel by a feeder. This ensures a uniform and controllable feed rate.
2.Melting and Plasticizing Stage: The barrel is heated by its integrated heating system while the screw rotates at high speed. The raw materials are agitated and compressed, causing them to melt under the combined effect of high temperature and pressure and form a homogeneous melt.
3.Homogenization and Conveying Stage: The screw continuously advances the melt toward the die. During this process, the melt undergoes further mixing and homogenization to ensure consistent density and viscosity, laying a solid foundation for the subsequent shaping process.
4.Shaping and Solidification Stage: The homogenized melt is forced through a custom designed die to form the desired cross-sectional shape. It then undergoes a cooling process to solidify and set into shape, resulting in the final continuous product.
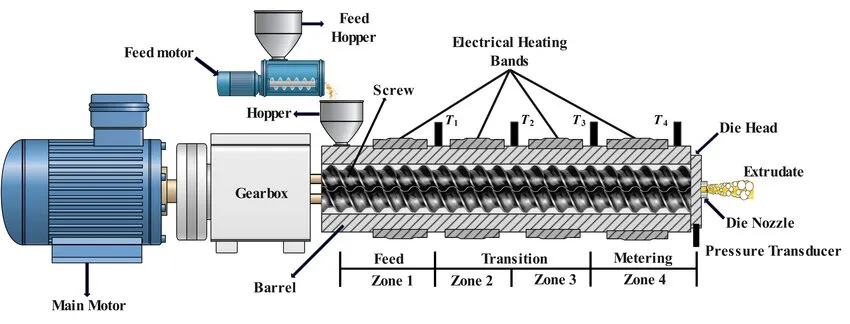
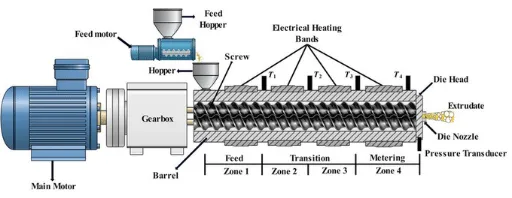
1.Screw: Its primary functions are to convey, mix, compress, and plasticize materials. Through a three section design consisting of a feeding section, compression section, and metering section, it gradually transforms materials from a solid state to a molten state. Its stepless adjustable speed allows for precise control over the material’s dwell time inside the barrel, ensuring adequate plasticization and a stable extrusion process.
2.Barrel: Working in conjunction with the screw, it forms a sealed plasticizing chamber. Its core function is to provide stepwise heating to materials via a zoned temperature control system. Simultaneously, it relies on a cooling circuit to regulate temperature, preventing material degradation due to local overheating. This ensures uniform plasticization of materials and provides stable conditions for subsequent extrusion molding.
3.Hopper: Used for storing raw materials such as pellets and powders, it features real time level monitoring to avoid material shortages. It is also synchronized with the main unit through a variable frequency feeding mechanism, enabling precise control over the feeding rate and ensuring uniform material supply. Additionally, it can be connected to a drying system to reduce the moisture content of raw materials, preventing adverse effects on plasticization quality.
4.Die: Its core role is to determine the cross sectional shape of the final product. Optimized internal flow channels ensure that the molten material is evenly distributed and extruded smoothly. Equipped with a temperature compensation device, it controls dimensional deviations of the product. It also features easy disassembly and assembly as well as convenient maintenance, allowing for quick replacement to adapt to the production of products with different specifications.
5.Control System: Responsible for real time monitoring and adjustment of key process parameters such as barrel temperature, screw speed, and melt pressure, it includes an automatic overpressure protection function to prevent equipment failures. It can store process parameters and interface with production management systems to enable data traceability, ensuring continuous and stable equipment operation as well as consistent product quality.
Types of Extruders by Structure
Based on differences in the number of screws and structural design, extruders are primarily classified into two main categories: single screw extruders and twin screw extruders. Each category has distinct advantages in terms of operational characteristics, suitable materials, and application scenarios, as detailed below:
- Single Screw Extruders: Featuring a core structure of a single continuous screw, the flight depth and screw pitch are optimally designed in three sections (feeding, compression, and metering). These extruders offer excellent operational stability and low failure rates. They are suitable for processing commodity plastics such as polyethylene and polypropylene, as well as standard rubber materials. Capable of meeting the production requirements for conventional products like pipes and films, single screw extruders are the mainstream choice for small and medium scale production and regular material processing due to their simple structure, easy operation, and low maintenance costs.
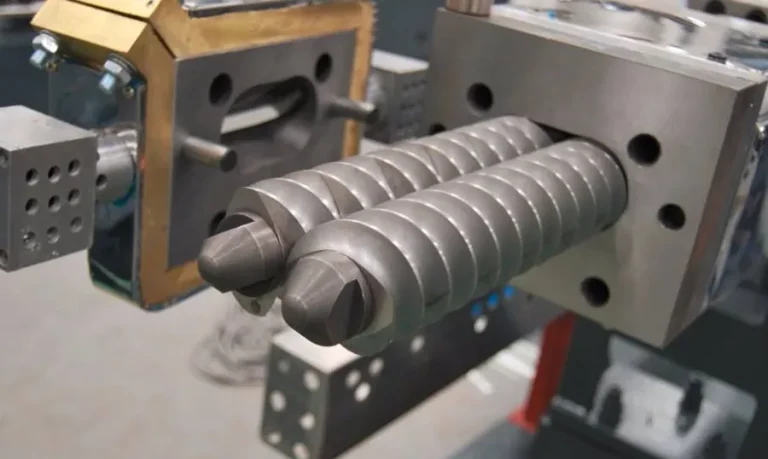
- Twin Screw Extruders: Utilizing a structure of two intermeshing screws, these extruders are further divided into co rotating and counter rotating types based on the direction of meshing. They possess enhanced shearing and mixing capabilities. Twin screw extruders can effectively process high viscosity, high filler loading, and modified composite materials such as glass fiber reinforced plastics and flame retardant modified materials. The plasticization uniformity of materials is far superior to that of single screw models, and they offer higher production efficiency. These extruders are ideal for large scale industrial production and high end custom material processing scenarios.
Applications of Extruders
1.Plastics Industry: This is the most widely used field for extruders. Extruders can produce products such as PE water supply pipes, PVC drainage pipes, PVC door and window frames, decorative profiles, BOPP packaging films, and polypropylene fibers. Single screw extruders are mostly used for processing commodity plastics while twin screw extruders are suitable for modified plastics and high end film production. The resulting products are widely applied in municipal engineering, daily necessities manufacturing, and industrial parts processing.
2.Rubber Industry: Extruders are mainly used to manufacture rubber hoses including hydraulic hoses and oil delivery hoses, automotive weatherstripping, construction waterproof membranes, and industrial rubber sheets. Extruders enable continuous plasticization and molding of rubber materials, ensuring uniform product density and precise dimensions. This meets the weather resistance and sealing performance requirements for rubber products in the automotive, construction, and machinery sectors.
3.Building Materials Industry: Extruders are core equipment for processing products such as PVC floor tiles, bamboo wood fiber integrated wall panels, thermal insulation profiles, and plastic grids. The extrusion process endows building materials with excellent compressive strength, moisture resistance, and sound insulation properties. With high production efficiency and controllable costs, extruders align with the modern construction industry’s demands for environmental friendliness and modular construction.
4.Packaging Industry: Extruders cater to the packaging needs of food, pharmaceutical, chemical and other fields. They can produce food grade packaging films, blow molding preforms, express packaging straps, and composite packaging substrates. Packaging materials processed by extruders combine sealing performance, corrosion resistance, and printability, meeting the packaging safety, fresh keeping, and appearance requirements of different industries.
Global Market Demand and Trends for Extruders
Driven by the expansion of the plastic processing, automotive, and construction industries, the global market demand for extruders continues to grow. Meanwhile, the rising demand for customized and high precision products has further boosted the need for high end extruders.
Energy conservation and environmental protection represent the core development trends, with a growing number of extruders adopting energy efficient motors and temperature control systems. In addition, intelligent upgrading which integrates the Internet of Things and automation technologies to enable real time monitoring and remote control is emerging as the industry mainstream. This trend helps improve production efficiency and operational stability.