Twin Screw Extruders: A Basic Understanding and Definition
The twin-screw extruder is a core equipment in the industrial material processing field. Its efficient material handling capacity and wide adaptability make it a key support for numerous production processes. Whether optimizing production workflows, improving product quality, or conducting precise equipment selection and layout, establishing a basic understanding of this machine is crucial. This article will systematically sort out the core basic information of the twin-screw extruder from the perspectives of definition, working principle, core components, and application scenarios.
Definition of Twin Screw Extruder
A twin screw extruder is a continuous industrial processing equipment that uses two intermeshing or non intermeshing screws. Through the synergistic effect of high speed rotation within a closed barrel, it completes material conveying, mixing, melting, plasticizing and extrusion molding. Compared with single screw extruders, it has more advantages in material processing uniformity, efficiency and adaptability to complex materials, making it a core equipment in many processing fields.
Working Principle of Twin Screw Extruder
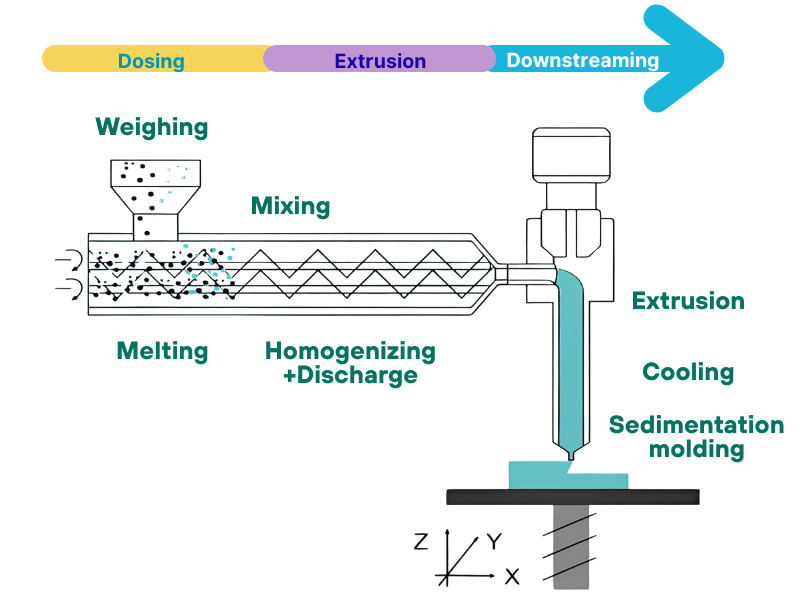
The core working principle of a twin screw extruder lies in the coordinated rotation of two screws combined with the barrel to achieve the processing and transformation of materials in stages. The entire process is continuous and controllable, with each stage closely connected to ensure the final product quality.
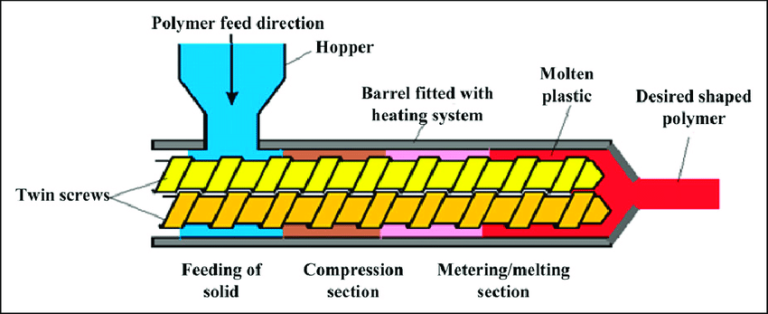
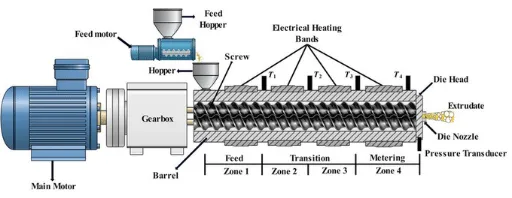
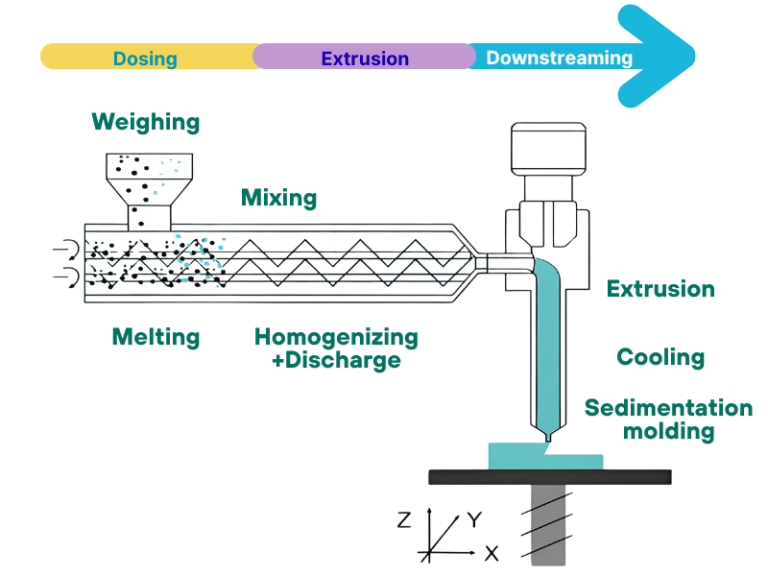
- Feeding stage: Materials steadily enter the barrel through a dedicated feeding device. The two screws use the pushing force of the spiral grooves to transport the materials evenly into the barrel, ensuring the continuity and stability of feeding and laying a foundation for subsequent processing.
- Compression and mixing stage: As the flight depth of the screws gradually decreases, the materials are squeezed to achieve volume compression. At the same time, under the action of barrel heating and screw rotation shear, the materials gradually soften and melt, and different components are fully mixed uniformly during this process.
- Plasticization and homogenization stage: The molten materials continue to be transported forward. Through further shearing, stirring and precise temperature adjustment by the screws, complete plasticization is achieved. The temperature and composition uniformity of the materials meet the processing standards and meet the molding requirements.
- Extrusion molding stage: The uniformly plasticized materials are pushed to the die head. Through the specific die cavity inside the die head, the products with the required cross-sectional shape are finally extruded, completing the entire processing flow.
Main Components of Twin Screw Extruder
The stable operation of a twin screw extruder relies on the coordinated cooperation of various core components. Below is a detailed introduction to the functions, roles and core parameters of key components such as screws, barrels and feeding devices, helping to quickly grasp the core value of each component.
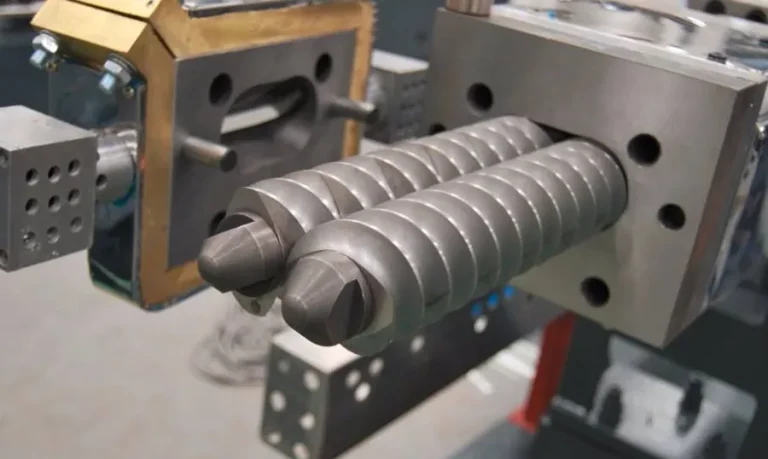
- Screws: The core working components, divided into feeding section, compression section and metering section by function. The spiral structure directly determines the material conveying and processing effect. Their meshing type (same direction or different direction), pitch, flight depth and other parameters need to be accurately matched according to processing requirements.
- Barrel: Cooperates with screws to form a closed processing space. The inner wall is equipped with heating and cooling devices for precise control of processing temperature. At the same time, it bears the extrusion force of materials and the acting force generated by screw rotation to ensure processing stability.
- Feeding device: Mostly adopts screw type or gravity type feeder. Its core function is to feed materials into the barrel continuously, uniformly and accurately, avoiding feeding fluctuations that affect processing quality and efficiency.
- Die head and mold: The die head is responsible for converging and stabilizing the pressure of molten materials, playing a transitional and guiding role. The mold directly determines the cross-sectional shape of the final product. Different specifications and models can be replaced according to production needs to adapt to diverse production scenarios.
- Drive system: Composed of motor, reducer and other components, it provides stable power for screw rotation. By adjusting the rotation speed, the material conveying speed and processing rhythm can be accurately controlled to adapt to the processing needs of different materials.
Application Scenarios of Twin Screw Extruder
With its efficient material handling capacity and wide adaptability, the twin screw extruder has been extensively applied in multiple industrial fields. Below is a detailed overview of its specific applications in core industries such as plastic processing and rubber industry, demonstrating its diverse application value.
- Plastic processing industry: Widely used in core processes including plastic modification (filling, reinforcement, flame retardancy, toughening, etc.), extrusion molding of plastic pipes profiles and sheets, as well as recycling and reprocessing of waste plastics.
- Rubber industry: Utilized for rubber mixing, plasticization and extrusion molding of rubber products, such as large scale production of rubber seals, hoses, gaskets and other products.
- Food processing field: Suitable for grain puffing, mixing and molding of food raw materials, such as the processing of breakfast cereals, pet food, snacks and other products, ensuring product quality and production efficiency.
- Biodegradable materials field: Targeting the characteristics of biodegradable plastics, it achieves efficient plasticization and molding processing, supporting the large scale production of environmentally friendly products such as biodegradable films, tableware and packaging materials.
- Chemical industry: Used for mixing, reaction and molding of chemical raw materials, such as the processing of resins, coating binders and special chemical additives, improving material uniformity and subsequent processing performance.
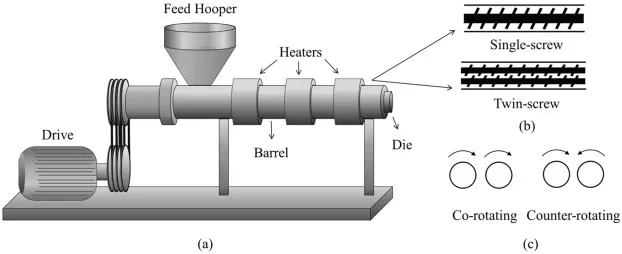
Single screw extruders and twin screw extruders have significant differences in structural design, processing performance and application scenarios. Below is a comparison from key dimensions to help accurately distinguish their characteristics:
- Core structure: A single screw extruder has only one working screw with a relatively simple structure. A twin screw extruder is equipped with two intermeshing or non intermeshing screws, featuring a more complex structure and higher requirements for coordinated operation.
- Processing efficiency: Single screw extruders rely on friction for material conveying, resulting in lower efficiency. Twin screw extruders achieve stable and more efficient material conveying through the coordinated pushing of screws, making them particularly suitable for high capacity demand scenarios.
- Material adaptability: Single screw extruders are more suitable for single easy to process materials such as ordinary plastic pellets. Twin screw extruders have stronger processing capabilities for complex materials such as multi component mixed materials and high filler modified materials, with superior mixing uniformity.
- Operation difficulty and maintenance: Single screw extruders have a simple structure, lower operating threshold and lower maintenance costs. Due to their complex structure, twin screw extruders require higher operational skills and incur relatively higher subsequent maintenance costs.
- Cost investment: Single screw extruders have low manufacturing costs and low initial investment. Twin screw extruders have high technical content, high manufacturing costs and greater initial investment.
How to Choose the Right Single Screw Extruder
Choosing the right single screw extruder must take into account core factors such as your own processing needs, material characteristics and production capacity planning. Below are the key selection considerations:
- Clarify processed materials: Select a suitable screw type based on material characteristics such as hardness, viscosity and presence of impurities. For example, deep flight screws are required for processing high viscosity materials, and wear resistant screws are needed for materials containing impurities.
- Define production capacity requirements: Determine the extruders screw diameter and speed range according to the production scale. Generally, the larger the screw diameter and the higher the speed, the higher the production capacity. Avoid excess or insufficient capacity.
- Consider processing precision: If high precision products such as precision pipes and films need to be produced, choose models equipped with a precision temperature control system and stable drive system to ensure the stability of the processing process.
- Evaluate operation and maintenance conditions: Make a selection based on workshop space and operators technical proficiency. When space is limited or operators have insufficient experience, prioritize models with a compact structure and easy operation.
- Control budget range: Balance equipment performance and cost according to your own budget. Prioritize cost effective models while considering the equipments durability and ease of subsequent maintenance.