Differences Between Single Screw and Twin Screw Extruders
Single screw extruders and twin screw extruders are the mainstream equipment types in the field of industrial material molding, with significant differences in their application scenarios, performance characteristics, and cost structures. Understanding these differences enables manufacturing enterprises to select equipment that aligns with their production requirements. For distributors, a clear grasp of these distinctions allows them to better match user needs, thereby improving order conversion rates and customer satisfaction.
This article will systematically introduce the core characteristics of single screw and twin screw extruders, break down their key differences from multiple dimensions including physical structure, operational capabilities, and cost control, and provide targeted equipment selection recommendations. It aims to assist you in making optimal decisions based on your actual needs.
About Single Screw Extruders
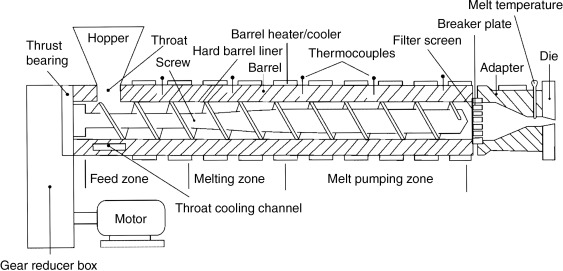
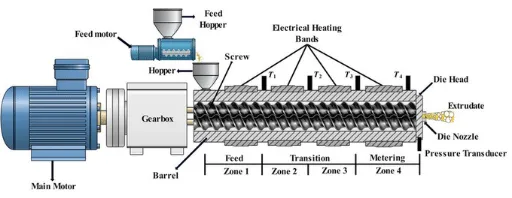
The single screw extruder is a fundamental model in the extruder field. Its core structure consists of a single screw, barrel, hopper, drive system, and temperature control system, featuring a compact and simple overall design with high technical maturity.
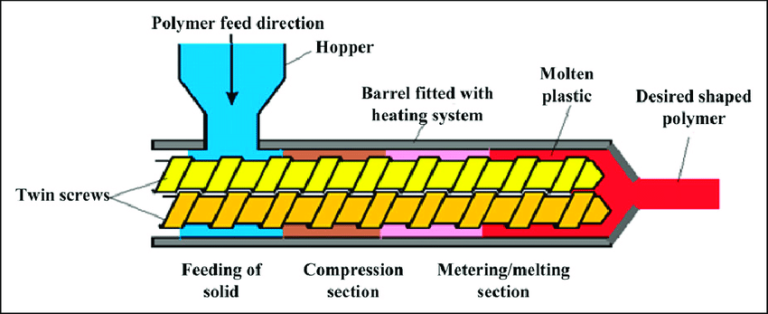
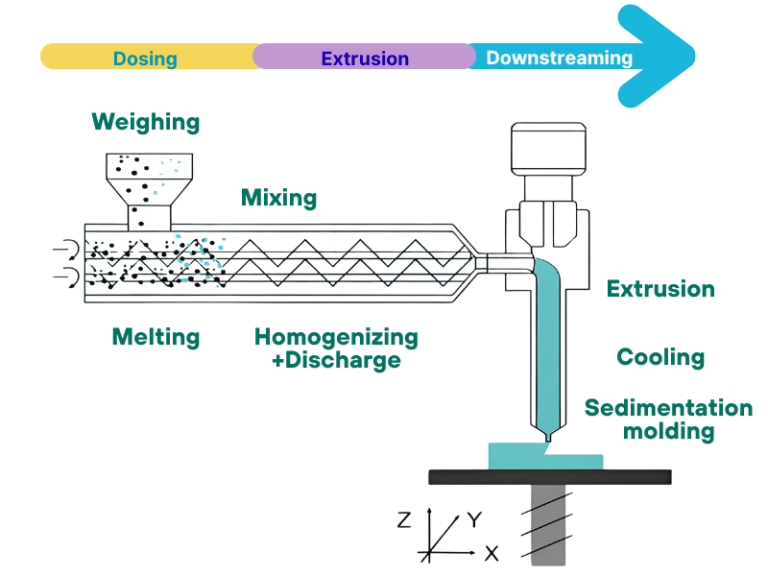
In terms of working principle, the single screw extruder completes material processing through a “frictional conveying” mechanism: relying on the friction difference between the material and the inner wall of the barrel, as well as between the material and the screw surface, the raw material is driven to move forward along the spiral direction of the screw. Meanwhile, under the action of the screw’s three-section structure (feeding section, compression section, metering section), the raw material is gradually compressed, plasticized, and melted, ultimately being extruded and shaped through a die.
Its core advantages lie in easy operation, stable operation, and low maintenance costs. It has relatively low technical requirements for operators and can stably meet the continuous molding needs of conventional materials such as general-purpose plastics. It is the mainstream choice for numerous basic industrial processing scenarios.
About Twin Screw Extruders
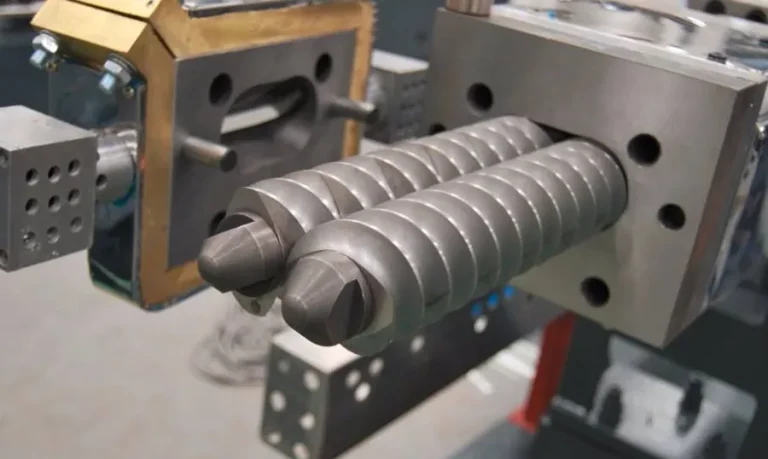
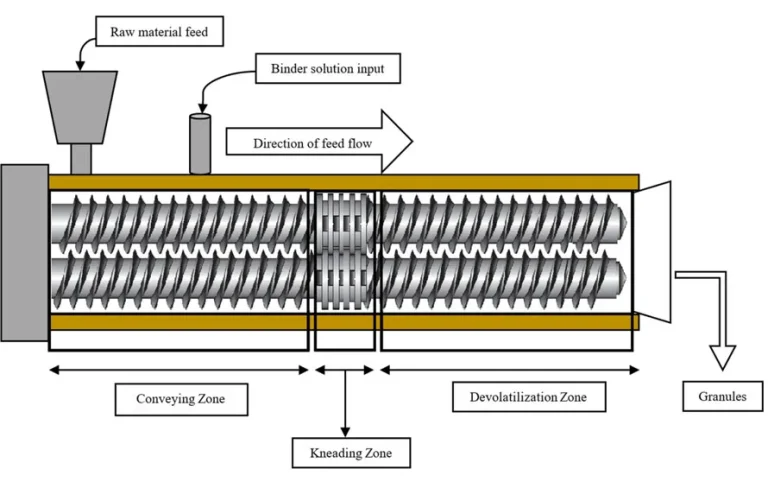
The twin screw extruder takes two intermeshing screws as its core components, paired with a high-precision barrel, customized die head, and intelligent temperature control and transmission system. Its overall structural complexity is higher than that of single screw extruders.
Its core working principle is “intermeshing positive conveying”: when the two screws rotate synchronously, the raw materials are forced forward through the meshing action of the spiral blades, without relying on the friction between the material and the barrel, resulting in stronger conveying stability. According to the direction of screw rotation, it can be divided into two types: co-rotating twin screw extruders (focusing on material mixing uniformity and higher plasticization efficiency) and counter-rotating twin screw extruders (focusing on improving extrusion pressure and adapting to high-viscosity materials).
Compared with single screw models, the twin screw extruder’s core advantages include high plasticization efficiency, excellent material mixing uniformity, and the ability to process materials with complex characteristics such as high viscosity, high filling rate, and heat sensitivity. It is the core equipment in high-end processing fields and special material molding.
Differences Between Single Screw and Twin Screw Extruders
1.Differences in Physical Structure
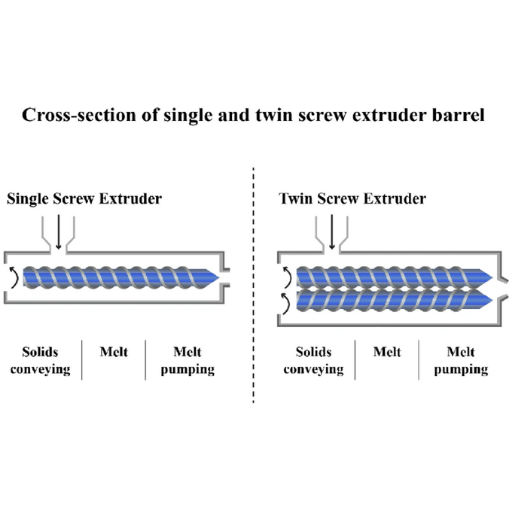
- Core Component Configuration: A single screw extruder is equipped with only one independent screw, with a relatively large gap between the screw and the barrel, and no intermeshing structure. A twin screw extruder is equipped with two intermeshing screws, featuring extremely small gaps between the screw and barrel as well as between the two screws, requiring precise control of intermeshing accuracy and speed synchronization.
- Overall Structural Complexity: A single screw extruder has fewer core components, lower assembly difficulty, and a relatively compact size. A twin screw extruder requires a high-precision transmission system and synchronization control system, resulting in a more complex structure and higher requirements for assembly and commissioning.
2.Differences in Operational Capabilities
- Conveying and Plasticization Efficiency: Single screw extruders rely on frictional conveying, so conveying efficiency is greatly affected by material properties, and plasticization speed is relatively slow, making them suitable for molding processing of single raw materials. Twin screw extruders adopt forced intermeshing conveying, ensuring stable and higher conveying efficiency. The shearing and mixing effects of the twin screws can significantly improve plasticization efficiency, enabling composite processing of multiple raw materials.
- Material Adaptability Range: Single screw extruders are mainly suitable for general-purpose plastics such as polyethylene (PE) and polypropylene (PP), as well as single raw materials with low processing difficulty. Their processing capacity for high-filling, high-viscosity, and heat-sensitive materials is limited. Twin screw extruders can widely adapt to materials with complex characteristics such as PVC, modified plastics, filled plastics, and biodegradable plastics, offering a broader adaptability range.
- Molding Precision: Limited by conveying stability, single screw extruders produce finished products with relatively average dimensional accuracy and surface uniformity. Twin screw extruders achieve more uniform conveying and plasticization, which can effectively improve the dimensional accuracy and surface smoothness of finished products while reducing molding defects.
3.Differences in Cost Structure
- Procurement Cost: Single screw extruders have a simple structure and low manufacturing cost, resulting in a relatively low equipment procurement threshold. Twin screw extruders require high precision for core components and complex supporting systems, leading to higher manufacturing costs. Their procurement price is usually 2 to 5 times that of single screw models.
- Operating Cost: Single screw extruders have relatively low energy consumption and low technical requirements for operators, resulting in lower labor costs. Twin screw extruders consume more energy and require professional and technical personnel for operation and commissioning, leading to higher labor and energy costs compared to single screw models.
4.Differences in Operation and Maintenance Difficulty
- Maintenance Complexity: Single screw extruders have fewer core components and a simple structure. Daily maintenance mainly focuses on cleaning and wear inspection of the screw and barrel, with simple maintenance procedures and long cycles. Twin screw extruders require high intermeshing precision for screws and have multiple supporting systems. Maintenance covers multiple links such as checking the intermeshing gap of screws, lubricating the transmission system, and calibrating the control system, resulting in higher maintenance complexity and shorter cycles.
- Spare Part Acquisition and Replacement: Core spare parts such as screws and barrels of single screw extruders have strong versatility, wide acquisition channels, and low replacement difficulty. Screws of twin screw extruders need to be paired, with high precision requirements for spare parts. The acquisition cycle is relatively long, and both replacement cost and difficulty are higher.
5.Differences in Application Scenarios
- Application Scenarios of Single Screw Extruders: Widely used in the field of basic plastic processing, they can produce conventional products such as ordinary pipes (e.g., PE water supply and drainage pipes), films (e.g., PE heat shrinkable films), wire and cable coating, and ordinary profiles. They are commonly found in basic production lines of small and medium-sized processing enterprises, suitable for mass production scenarios with low requirements for product precision.
- Application Scenarios of Twin Screw Extruders: Focusing on high-end and complex processing fields, they can be used to produce high-end products such as modified plastic pellets, PVC special profiles, biodegradable plastic products, high-filling composite pipes, and special films. They are commonly used in large-scale processing enterprises and special material production enterprises, suitable for customized production scenarios with strict requirements for product quality and performance.
Which Extruder Best Fits Your Needs?
If you process general-purpose plastics (such as polyethylene and polypropylene), focus on single raw materials and conventional molded products (e.g., ordinary pipes, films, wire coating), and prioritize minimal equipment procurement and operating costs along with ease of operation, a single screw extruder will fully meet your requirements.
If you need to process materials with complex characteristics such as high-viscosity, high-filling, modified, or heat-sensitive materials (e.g., PVC, modified plastics, biodegradable plastics), or if you pursue high production capacity and high finished product precision with products of high added value, a twin screw extruder is recommended.
If you are a small or medium-sized enterprise with limited production scale, tight budget constraints, and no immediate need for processing complex materials, a single screw extruder is the preferred choice. It can effectively control initial investment and operational costs.
If you are a large enterprise with diverse production scenarios requiring coverage of high-end and complex material processing, and if you value production efficiency and finished product quality, a twin screw extruder is better suited to your long-term development needs, helping to enhance core competitiveness.
If your production team has limited technical capabilities and you wish to reduce equipment maintenance difficulty and minimize downtime losses, the stability and low-maintenance characteristics of a single screw extruder offer distinct advantages. If you have a professional technical operation and maintenance team, you can fully leverage the performance advantages of a twin screw extruder.