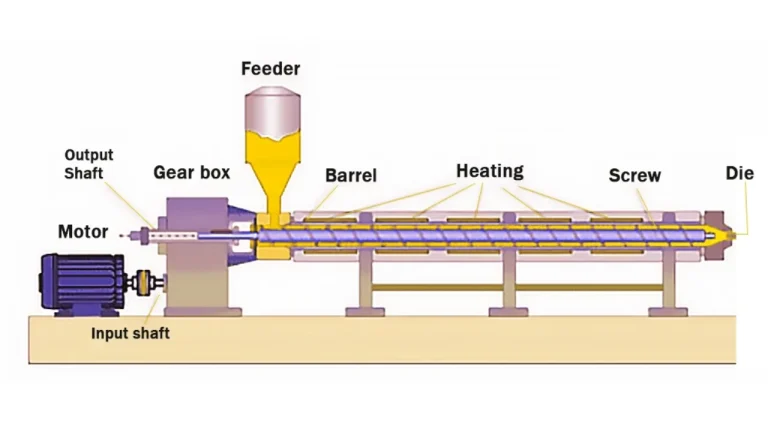
Detailed Single Screw Extruder Design Diagram
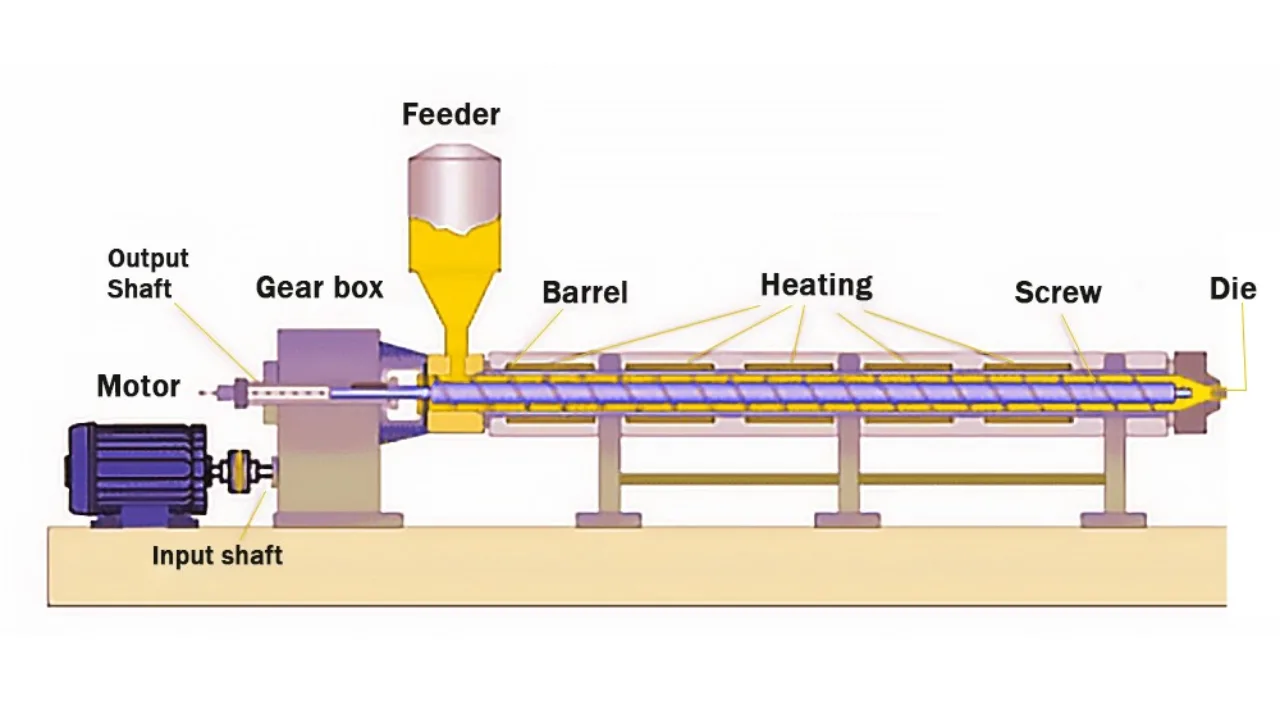
For overseas distributors, understanding the design drawings and core structure of single screw extruders enables them to quickly address customer technical inquiries, grasp the equipment’s structural advantages, and enhance their sales messaging. For manufacturing enterprises, a clear understanding of the design and core structure of single screw extruders allows for the selection of equipment with better compatibility to their specific production requirements. This article will start with an overview of industrial design drawings, break down core components, and outline the main parts, working principles, and industry applications of single screw extruders, providing you with a practical technical reference.
Key Components of Single-Screw Extruders
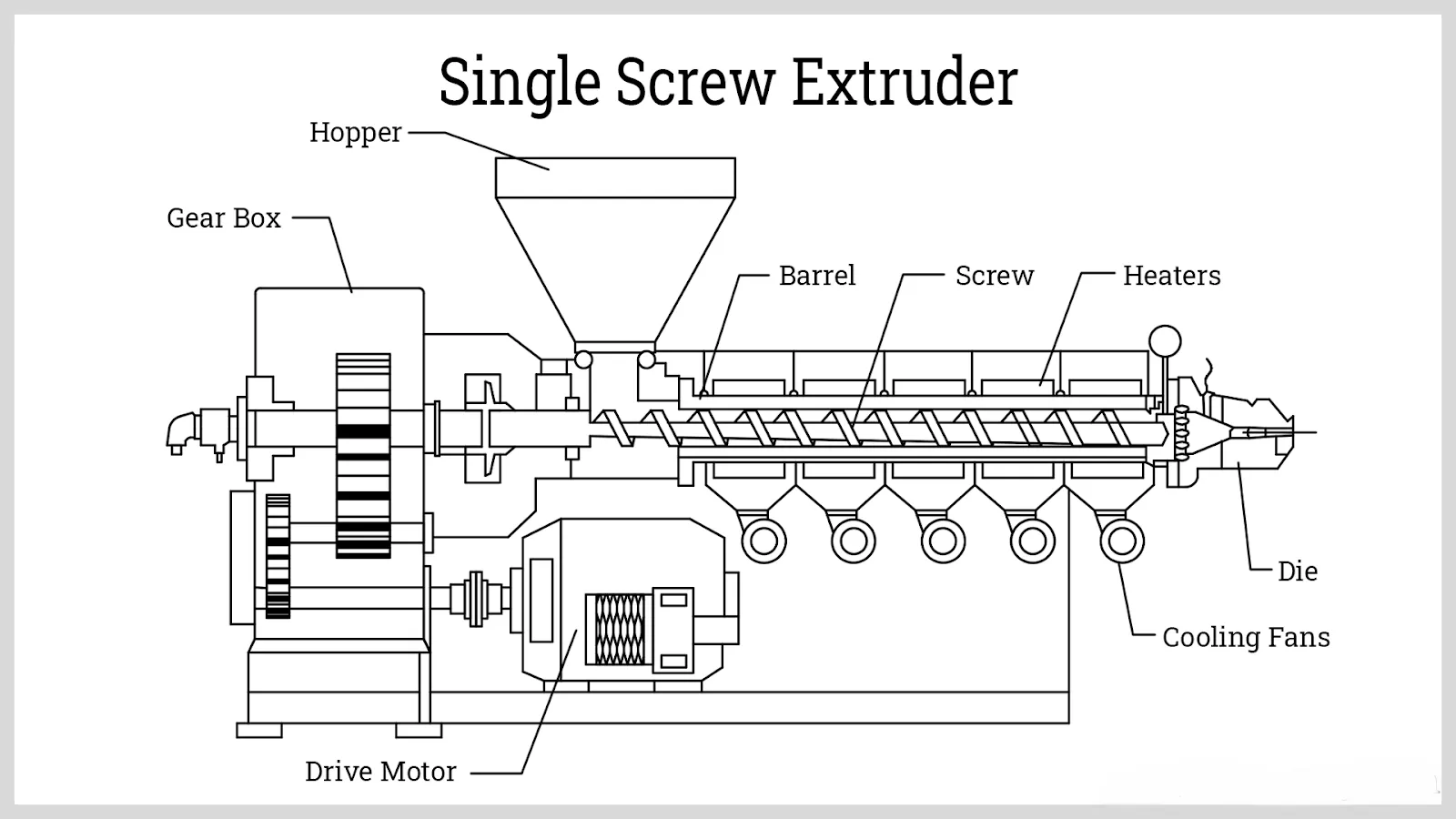
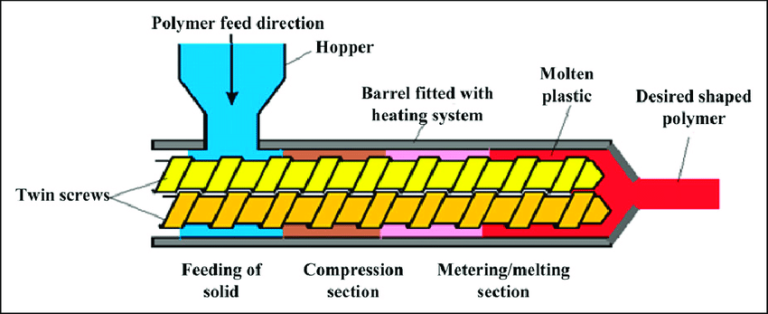
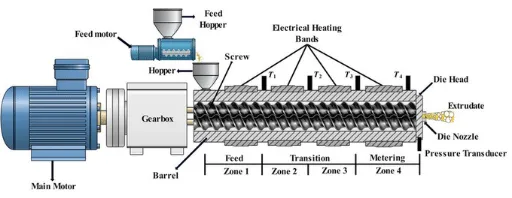
- Screw: As the core moving component of the equipment, it is clearly divided into three functional sections: the feed section, compression section, and metering section. The length ratio, pitch, and flight depth gradient of each section are all engineered with precise proportions. Industrial-grade screws are typically fabricated from high-strength wear-resistant alloys. Through optimized flight channel design, they not only significantly enhance material conveying efficiency but also ensure uniform plasticization, enabling flexible adaptation to processing scenarios involving materials of varying viscosities.
- Barrel: It forms a sealed working chamber through tight coordination with the screw. Stringent tolerances are applied to its inner diameter, effective length, and the clearance between the barrel and the screw. Zoned heating and cooling units are mounted on the outer surface of the barrel, which is constructed from materials that balance excellent thermal conductivity and wear resistance. By rationally dividing temperature control zones, the barrel ensures that materials undergo a smooth, gradual transition from a solid state to a molten state during forward conveyance, laying a solid foundation for subsequent plasticization and forming.
- Die Head and Mold: These are the core components of the extrusion forming process. The flow channel structure of the die head and the outlet dimensions of the mold can be customized to suit different product types, such as pipes, profiles, and films. The scientific design of the flow channel curvature directly impacts the uniformity of melt flow, while mold precision determines critical product metrics including surface quality and wall thickness tolerance. This component is a vital link in ensuring product compliance with specifications.
- Drive System: Composed of three core components—an electric motor, a reducer, and a coupling—it must be precisely matched to the screw’s speed adjustment range to deliver stable, controllable power output for screw rotation. The overall design fully accounts for the complex operating conditions of industrial environments, balancing protection and heat dissipation requirements. It effectively ensures the stability of the equipment during long-term continuous operation and reduces the probability of unplanned downtime due to malfunctions.
- Auxiliary Systems: This category encompasses three key subsystems: temperature control, lubrication, and feeding. These three systems work in synergy to support the efficient operation of the extruder. The temperature control system enables precise regulation of temperatures across all zones; the lubrication system effectively reduces frictional wear of components; and the feeding system ensures a continuous, stable supply of materials. Collectively, this system directly impacts the equipment’s operational efficiency and service life, serving as a critical safeguard for maintaining production continuity.
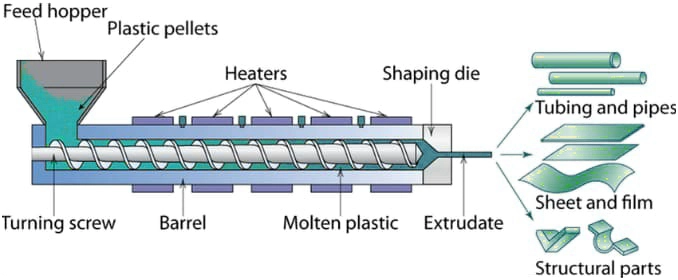
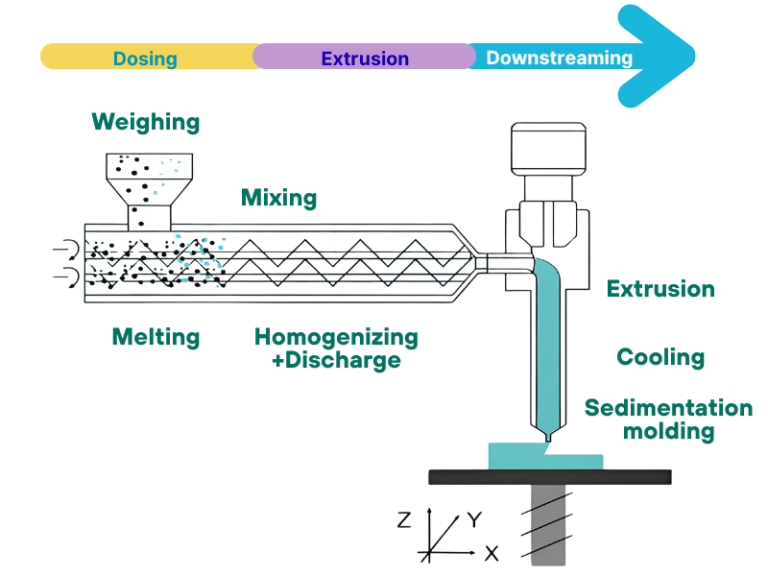
- Feeding and Preheating Stage: After materials enter the barrel from the hopper, they are conveyed forward by the rotational thrust generated by the feed section of the screw. The flight channels in this section are designed to be relatively deep, enabling stable material feeding. Simultaneously, the heating units in the front section of the barrel activate for preheating, which initially softens the materials in preparation for subsequent plasticization. The rationality of temperature control zone division as specified in the design drawings directly impacts the performance of this stage.
- Compression and Melting Plasticization Stage: As materials move into the compression section, the progressively narrowing flight channel space (as depicted in the design drawings) subjects them to continuous compression, leading to a gradual increase in material density. Combined with temperature elevation in the middle section of the barrel, the materials undergo gradual melting under the synergistic effect of pressure and temperature. This process also removes internal air bubbles and impurities, ultimately forming a homogeneous and dense melt. The clearance design between the screw and the barrel is a critical factor that determines plasticization efficiency.
- Metering and Stable Extrusion Stage: Once the melt enters the metering section, the depth of the flight channels remains constant. The screw precisely controls the melt’s conveying speed and pressure through calibrated rotation, performing a secondary homogenization process to ensure consistent flow properties. The melt is then steadily pushed to the die head and shaped into the preset profile by the mold. The die head flow channel parameters specified in the design drawings are key to ensuring extrusion stability.
- Regulation and Adaptation Stage: Through the temperature control, speed regulation, and extrusion pressure adjustment interfaces marked in the design drawings, real-time adjustments are made to the temperature of each barrel zone, screw rotational speed, and extrusion pressure. These adjustments enable the extruder to adapt to the characteristics of different materials (e.g., heat-sensitive or high-viscosity materials) and meet specific product specification requirements. This ensures a continuous and stable extrusion process, thereby improving the product qualification rate.
- Plastics Processing Industry: Widely used in production scenarios such as plastic pipes, profiles, films, wire coating, and pelletizing. For example, by optimizing the screw structure and die head mold based on design drawings, it is possible to manufacture products like PVC drain pipes, PE water supply pipes, and plastic door and window profiles, meeting the fundamental needs of the construction, municipal, and home appliance industries.
- Packaging Industry: Suitable for the production of packaging films, strapping bands, preforms for plastic containers, and composite packaging materials. Leveraging the adjustable screw speed and temperature control system specified in design drawings, it can produce packaging films of varying thicknesses, flexibility, and sealing performance, catering to the packaging, protection, and fresh-keeping needs of food, pharmaceutical, and industrial products.
- Building Materials Industry: Utilized for the extrusion molding of building materials such as underfloor heating pipes, decorative trim, plastic grids, and waterproof membranes. The optimized screw compression ratio and barrel temperature control design in the drawings enhance the product’s compression resistance, aging resistance, and weather resistance, meeting the stringent requirements of construction projects for equipment stability and product quality.
- Specialty Materials Processing Industry: Can be adapted to the processing needs of rubber, modified plastics, composite materials, and recycled plastics through customized structural design. Examples include plastic coating for wires and cables, extrusion pelletizing of modified plastic granules, and production of environmentally friendly recycled plastic pipes, supporting the green and personalized development of the industry.