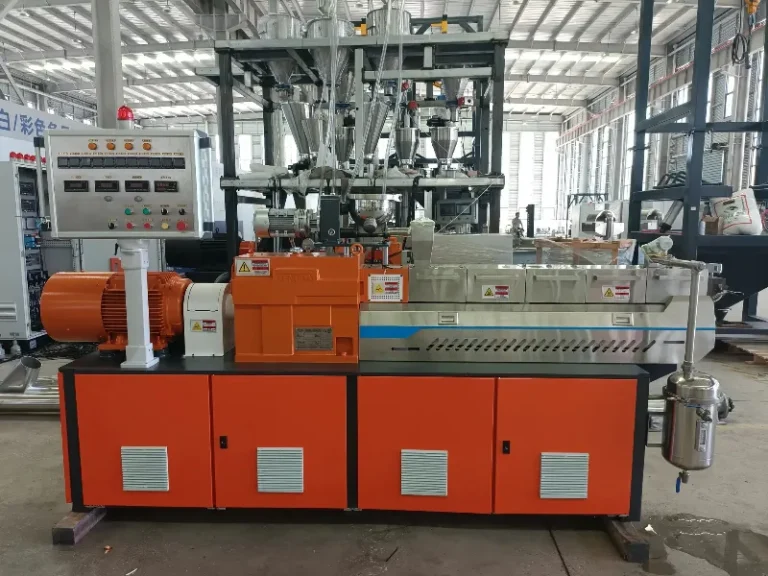
How Does a Twin Screw Extruder Work? Understanding Its Principle
Twin Screw Extruders are core equipment in industrial material processing. Their stable and efficient operation relies on scientific working principles. This article will break down their working principles, core components and application scenarios in detail, and compare the differences between them and Single Screw Extruders. It will help you fully master the equipment’s characteristics, provide professional references for equipment selection, operation and maintenance, and promotion, and support the improvement of production efficiency and product quality.
Working Principle of Twin Screw Extruders
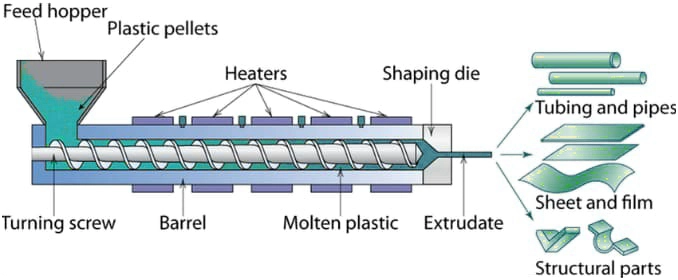
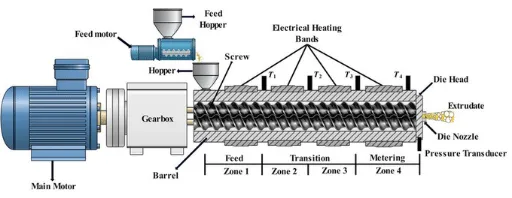
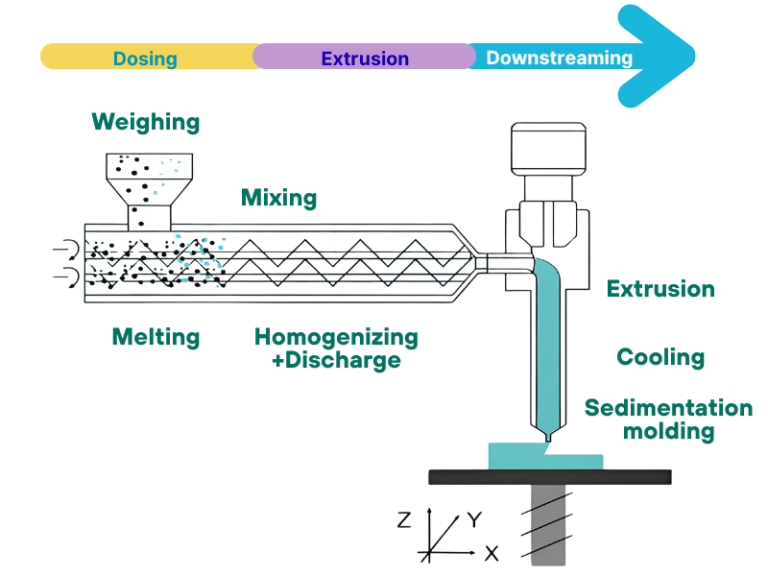
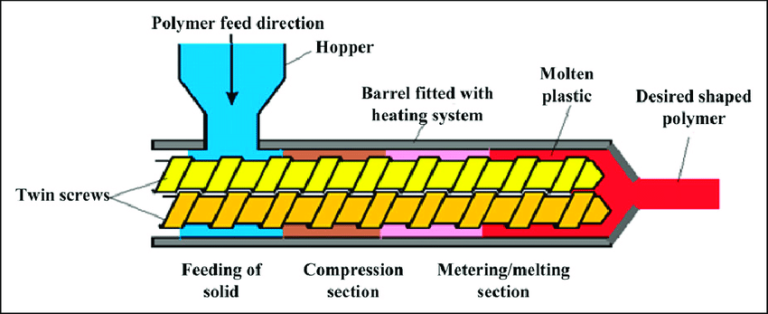
Twin Screw Extruders utilize two intermeshing or counter rotating screws to complete continuous material conveying, mixing, plasticization, pressurization and extrusion molding within the barrel. The entire process is coherent and controllable, with the core lying in the synergistic interaction between the screws and the barrel as well as the sequential coordination of each process step. Below are its core operational processes:
- Material Conveying Stage: After materials enter the barrel from the feeding device, the helical flights of the screws use rotational force to push the materials forward. Intermeshing screws can also achieve positive material conveying through tooth meshing, preventing material stagnation and ensuring conveying stability.
- Mixing and Plasticization Stage: During conveying, materials gradually reach a molten state due to barrel heating, screw shearing and frictional interaction between materials. At the same time, the helical structure of the screws continuously agitates and shears the materials, achieving uniform mixing of components and homogenization of material properties.
- Extrusion Molding Stage: The uniformly plasticized materials are continuously pressurized by the screws and pushed toward the die head. They form a predetermined shape through the specific cavity of the die and obtain the final product after cooling and setting. The entire process allows for parameter optimization by adjusting screw speed and temperature.
Core Components of Twin Screw Extruders
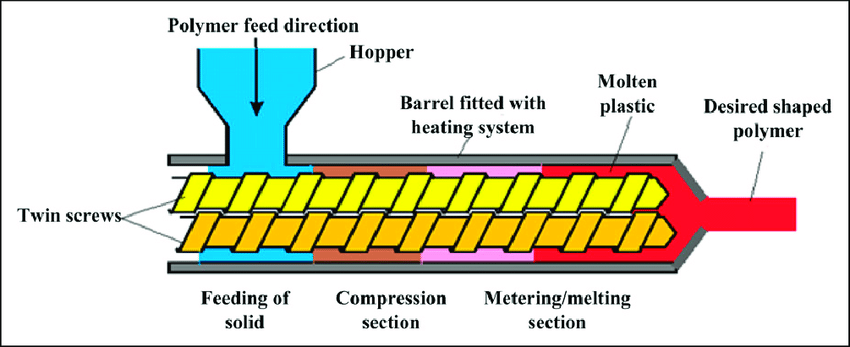
Core components form the foundation for twin screw extruders to execute their working principles and ensure operational performance. Each component has a clear division of labor and operates in synergy, directly influencing the equipment’s processing precision and stability.
Screws: The core moving components, categorized by function into feed sections, compression sections and metering sections. The lead, depth and tooth profile design of the helical flights determine material conveying efficiency and mixing effectiveness. Two common types are intermeshing and non intermeshing, tailored to meet different processing requirements.
- Barrel: Works in conjunction with the screws to form a sealed processing chamber. Its inner wall is fitted with heating and cooling devices for precise control of material processing temperatures. It also withstands material extrusion and friction, requiring high structural strength and wear resistance.
- Feeding Device: Responsible for uniformly and stably delivering materials into the barrel, preventing material caking or uneven feeding. It is typically equipped with a speed regulating mechanism to adjust the feed rate according to processing tempo, making it suitable for different material properties.
- Die Head and Mold: Critical components for material shaping. The die head functions to converge materials and stabilize pressure, while the mold’s cavity is designed based on product requirements, determining the cross sectional shape and dimensions of the final product.
- Temperature Control System: Uses heating coils, cooling water pipes and temperature control instruments to real time monitor and adjust the temperatures of the barrel, screws and die head. It ensures that materials maintain the optimal processing temperature range at all stages, safeguarding plasticization quality.
Common Application Scenarios of Twin Screw Extruders
With its high efficiency mixing and plasticization capabilities and stable processing performance, the Twin Screw Extruder is widely used across multiple industries. It can accommodate the processing needs of various material forms including solids, powders and granules.
Plastics Processing Industry: The core application field. It enables high efficiency production of all types of plastic products such as pipes, sheets, films and profiles. It excels in high precision processing tasks like plastic modification, filling and blending. Leveraging its superior mixing and plasticization capabilities, it precisely controls the uniformity of material components and enhances product mechanical properties — for example, increasing the strength of reinforced polypropylene and improving the flame retardant stability of flame retardant plastics. It meets the stringent requirements of high end plastic products in industries such as automotive, home appliances and packaging.
1.Food Processing Industry: Suitable for the production of grain puffed foods, pet food and nutritional meal replacements. Through controlled high temperature plasticization and extrusion molding processes, it not only achieves full material gelatinization to improve digestibility and absorption rates, but also precisely controls expansion ratio and molding precision to ensure consistent product texture. At the same time, it minimizes nutrient loss and features easy cleaning, complying with food industry hygiene standards and meeting the demands of large scale mass production.
2.Chemical Materials Industry: Widely used in the processing of rubber, coatings and adhesives, as well as the preparation of polymer materials, composite materials and functional masterbatches. Its positive conveying and high efficiency mixing characteristics enable rapid homogenization and reactive processing of multi component materials, shortening production cycles and improving product purity and performance stability. It is also suitable for high viscosity and easily agglomerated materials, effectively solving the pain points of uneven mixing and insufficient reaction associated with traditional equipment and facilitating the mass production of high end chemical materials.
3.Pharmaceutical and Building Materials Industries: In the pharmaceutical field, it is used for the high precision processing and molding of pharmaceutical excipients and sustained release preparation carriers. With its precise temperature control and clean design, it meets the strict pharmaceutical industry requirements for purity, sterility and molding precision. In the building materials field, it produces thermal insulation materials, waterproof membranes and new building material granules. It enhances material density and mechanical properties, endowing products with superior weather resistance and water resistance to adapt to various construction engineering scenarios.
The core difference between twin screw and single screw extruders stems from their screw structure design. This results in distinct disparities in material conveyance, mixing and plasticization, as well as suitable application scenarios, with each type offering unique advantages for specific use cases. Below are their specific differences:
- Material Conveyance Mechanism: Single screw extruders rely on frictional forces between the material and the screw barrel for material movement. This often leads to material stagnation and uneven conveyance. In contrast, twin screw extruders achieve positive material conveyance through screw intermeshing, delivering higher efficiency and greater stability. They are ideal for processing materials with high viscosity and poor flowability.
- Mixing and Plasticization Efficiency: The mixing and plasticization of single screw extruders depend primarily on barrel heating and screw shearing, which yields limited results and makes uniform mixing difficult to achieve. Twin screw extruders leverage the combined effects of screw intermeshing, shearing and agitation to deliver far higher mixing and plasticization efficiency, enabling precise homogenization of multi component materials.
- Suitable Material Range: Single screw extruders are better suited for processing materials with good flowability and simple compositions. Twin screw extruders, however, can handle materials with complex compositions, high viscosity and high mixing requirements such as multi component blends and filled modified materials, resulting in a much broader range of application scenarios.
- Operational Stability: Single screw extruders are highly susceptible to variations in material properties, which can cause frequent load fluctuations. The positive conveyance and synergistic operation design of twin screw extruders ensures more stable operation and higher processing precision, making them ideal for large scale continuous production.