Extruder as a modern industrial material processing important equipment, extruder technology level directly affects the production efficiency and product quality of plastic products, rubber products, composite materials and other fields. In this article, we have compiled a list of 11 global extruder manufacturers and analyzed their main products and advantages and disadvantages in detail.
Top 11 Extruder Manufacturers in the World
- UET TECH (China)
- Battenfeld Cincinnati (Austria)
- Bazzano (Italy)
- Beier Machinery (China)
- Davis-Standard (USA)
- ENTEK (USA)
- EREMA (Austria)
- Farrell Pomini (USA)
- KRAUSSMARPHY (Germany)
- JSW Shin Nippon Steel (Japan)
- YUE SHENG (China)
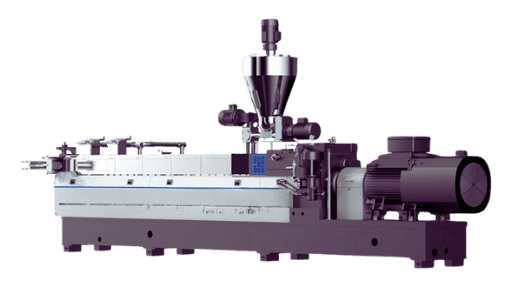
UET TECH (China)
- Established: 2014
- Strengths: With the world’s leading pipe extrusion technology, we can provide customized equipment according to customers’ actual needs.
- Main products: single/twin screw extruders, pipe production lines, film extrusion systems.
- Background: High quality extruder supplier in China, founded in 2014, has served more than 3,000 companies in more than
- 70 countries worldwide.
- Official website: UET machine website
Battenfeld Cincinnati (Austria)
- Established: 1943
- Strengths: The world’s leading pipe extrusion technology, its BCflow® die system can achieve ±0.1mm pipe tolerance for PE, PP, PVC and many other materials.
- Disadvantages: Higher equipment prices, higher procurement threshold for SMEs.
- Main products: single/twin-screw extruders, pipe lines, film extrusion systems.
- Background: The company is part of the Austrian Shenyang Steel Group, specializing in the research and development of plastics processing equipment, with a market share of more than 30% in the fields of municipal piping and automotive lightweighting.
- Official website: Battenfeld Cincinnati website
Bolzano (Italy)
- Founded: 1961
- Benefits: Leading-edge medical-grade extruder technology, its E-GO R series can process waste plastics containing 20% impurities and achieve 98% raw material utilization.
- Cons: Longer lead times for larger lines (about 6-8 months).
- Main products: Single-screw extruders, medical-grade pipes, plastic recycling equipment.
- Background: Family-owned company, headquartered in Treviso, Italy, with over 40% of the European medical consumables market.
- Official website: Bausano website
Beier Machinery (China)

- Established: 1998
- Advantages: Outstanding price/performance ratio, the price of its SJZ series conical twin-screw extruder is only 60% of the price of similar products in Europe.
- Disadvantages: Weak brand influence in the high-end market.
- Main products: PVC pipe production lines, wood-plastic extrusion equipment, PET recycling systems.
- Background: Headquartered in Zhangjiagang, Jiangsu Province, the company is listed on the New Third Board (stock code: 831784), with an annual export volume of more than 120 million U.S. dollars.
- Official website: Beier Machinery website
Davis-Standard (USA)

- Founded: 1848
- Strengths: Industry leader in rubber extrusion technology, with its DSR series of cold-feed extruders enabling continuous production of tire tread rubber at 30% higher efficiency.
- Cons: Innovation in plastics extrusion is lagging behind its European counterparts.
Key Products: Rubber extruders, blown film equipment, cable wrapping lines. - Background: Headquartered in Connecticut, U.S., the company has a 170-year history and is a core supplier to Michelin and Bridgestone.
- Official website: Davis-Standard website
ENTEK (USA)

- Founded: 1988
- Advantages: Global leader in battery diaphragm extrusion technology, with its third-generation Li-ion battery diaphragm production line reaching speeds of up to 260m/min and thickness tolerances of ±1%.
- Disadvantages: High maintenance costs (average annual maintenance costs of about 8% of the total equipment price).
- Key products: Li-ion battery diaphragm lines, microporous material extrusion systems.
- Background: Headquartered in Oregon, customers include Ningde Times and LG New Energy, with a market share of more than 35%.
- Official website: ENTEK website
EREMA (Austria)
- Founded: 1983
- Pros: No. 1 worldwide in plastics recycling technology, its VACUREMA® system produces food contact grade recycled PET with 99.5% purity.
- Disadvantages: high energy consumption for large recycling lines (approx. 0.8kWh/kg).
- Key products: Plastic recycling extruders, bottle-to-bottle recycling systems.
- Background: Headquartered in Ansfelden, Austria, the company owns 1,100 patents and recycles more than 20 million tons of plastic annually.
- Official website: EREMA website
Farrel Pomini (USA)

- Founded: 1916
- Pros: Leader in extruding high-viscosity materials, with its LCM series of twin-screw extruders handling difficult materials such as PUR and silicone.
- Disadvantages: Large equipment, 30% more floor space than similar equipment.
- Main products: twin-screw extruders, reaction extrusion systems, rubber mixing equipment.
- Background: Part of the Italian HF Group, headquartered in Connecticut, USA, serving companies such as ExxonMobil and DuPont.
- Official website: Farrel Pomini website
KraussMaffei (Germany)

- Founded: 1838
- Pros: Significant technological barriers to precision extrusion, PX series of single-screw extruders with ±0.3mm pipe tolerance to meet automotive lightweighting needs.
- Disadvantages: High equipment procurement costs (average price of a single unit exceeds 2 million euros).
- Main products: single / twin-screw extruders, composite pipe production lines, carbon neutralization extrusion systems.
- Background: The world’s largest rubber and plastic machinery group, headquartered in Munich, will launch a photovoltaic-powered extrusion line at its Qingdao site in 2024, reducing carbon emissions by 40%.
- Official website: KraussMaffei website
JSW Nippon Steel (Japan)

- Founded: 1956
- Pros: Leading in precision injection molding and extrusion integration technology, its JSW-EX series enables simultaneous injection and extrusion production, increasing efficiency by 25%.
- Weaknesses: Dependent on Japanese OEM technical support for equipment maintenance.
- Main Products: Integrated injection molding and extrusion machines, engineering plastics extruders.
- Background: Part of Japan’s JSW Group, headquartered in Tokyo, with a 25% market share in electronic components and medical devices.
- Official website: JSW Nippon Steel website
Yue Sheng (China)

- Established: 2006
- Advantages: Leading in foam extrusion technology, its EC series twin-screw extruders can produce foamed materials with density as low as 0.3g/cm³.
- Disadvantages: Complicated equipment operation, requires specialized training.
- Main products: foam extruders, wood-plastic composite production lines.
- Background: headquartered in Nanjing, Jiangsu Province, specializing in new “small giants” enterprises, annual revenue of more than 300 million yuan.
- Official website:Yue Sheng website
Key Factors in Selecting an Extruder Manufacturer
- Quality and reliability
Check the extruder manufacturer’s implementation of international standards (e.g., ISO, CE), as well as the processing accuracy and materials of core components, and confirm the service life of other customers’ equipment. - Technology adaptation and innovationWe need to ensure that manufacturers are able to meet the processing needs of a wide range of materials (plastics, rubber, composites, etc.), such as high-torque designs for highly viscous materials, high-speed extrusion technology for film production, and so on. Examples include high-torque designs for highly viscous materials, high-speed extrusion technology for film production, and more. We also look for integrated intelligence (e.g., IoT real-time monitoring, energy optimization systems) to help plants adapt to future capacity upgrades or process adjustments.
- Customization FlexibilityExtruder needs vary by industry (packaging, automotive, construction): food packaging may require corrosion-resistant barrels, while pipe production relies on screws with specific aspect ratios. Rather than push standardized products, quality manufacturers offer customized solutions based on specific capacity and material characteristics.
- Global aftermarket support networkEnsure that the manufacturer has a localized service team in the target market, a spare parts warehouse, and the ability to provide 24-hour remote diagnostics or on-site repairs within 48 hours-especially for high-capacity plants, where every hour of downtime can be costly.
- Compliance AdaptationEquipment needs to meet the regulatory requirements of the target market, such as CE marking for entry into the EU, UL safety standards for North America, and FDA material specifications for food contact equipment. Lack of compliance experience can lead to barriers to entry or subsequent manufacturing violations.
- Cost vs. long-term benefitsAvoid a purely price-oriented approach and evaluate the “acquisition cost + O&M cost + life cycle”: low-priced equipment may lead to higher long-term costs due to high energy consumption and frequent replacement of wear parts, while cost-effective equipment is often more advantageous in terms of energy consumption control and spare parts versatility.