As a fundamental piece of equipment in the field of plastics processing, single-screw extruders have become the core choice for small and medium-sized enterprises entering the industry and scaling up production, thanks to their simple structure and controllable costs. This article will provide an in-depth overview of their typical applications in sectors such as construction materials, packaging and daily necessities, and agriculture and horticulture, helping readers better understand the application value of single-screw extruders.
Common Applications of Single-Screw Extruders
1. Construction and Building Materials Industry
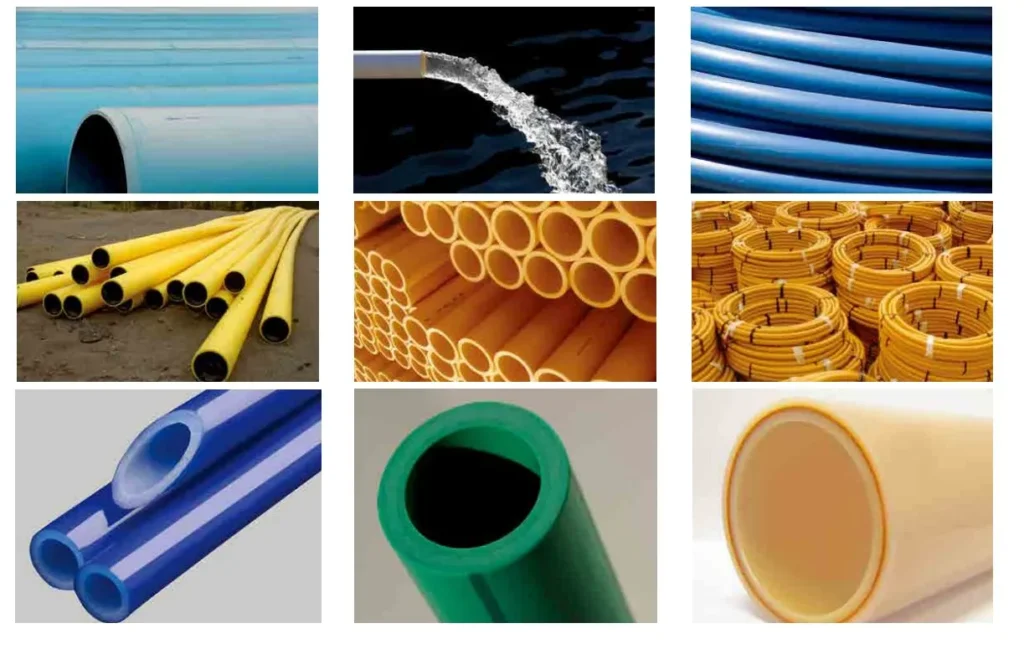
Commonly used for producing PE water supply pipes, PVC drainage pipes, and other tubular products, the continuous extrusion process ensures uniform wall thickness and smooth joints, making it suitable for municipal engineering and building drainage applications. It can also be used to manufacture PVC window frames, decorative strips, and other profiles. By using custom molds, the cross-section with slots can be formed in one go, eliminating the need for post-assembly processes, making it ideal for large-scale production.
2. Packaging and Daily Goods Industry
When processing PP packaging straps, the screw’s stable pushing force ensures uniform tensile strength, meeting bundling requirements. When producing PE film (such as food packaging film and shopping bags), adjusting the screw speed controls film thickness, ensuring uniform transparency and flexibility. Simple products like household cleaner tubes and simple plastic bottle preforms are also commonly produced using this method, as it does not require complex mixing functions, making it more adaptable.
3. Agriculture and Horticulture Sector
When extruding agricultural drip tubes, the continuous feeding characteristics of the single screw can be used to stably form pipes with small water outlets, meeting irrigation uniformity requirements; When producing plastic protective nets, seedling pots, and other products, its low material mixing requirements allow it to directly process recycled PE pellets, balancing cost and practicality; Plastic film strips and ropes used in greenhouses are also primarily produced using this method, meeting outdoor weather resistance requirements.
4. Basic Plastic Processing Applications
When processing pure plastic pellets (virgin material or simple recycled material), it can directly melt and extrude them into recycled pellets for reuse in downstream production; When producing furniture edge strips or simple irregular-shaped strips (such as refrigerator door seals), the flexibility of the molds allows for quick switching of cross-sectional shapes, making it suitable for small-to-medium-sized manufacturers with small-batch production changes; it can also produce plastic sheets (such as PVC thin sheets for ceilings), with stable plasticization capabilities ensuring a smooth surface.
5. Small-Scale and Customized Applications
When conducting small-batch pilot production of new plastic formulations in laboratories, its simple operation and easily adjustable parameters enable rapid verification of raw material compatibility. When producing low-precision cable insulation layers (such as the outer casing of ordinary wires), it can uniformly coat the conductor with melted plastic through screw extrusion, meeting basic insulation requirements. Small workshops producing plastic toy components, simple storage box blanks, and other products often rely on its cost-effective advantages to achieve mass production.

Core Advantages of Single-Screw Extruders
1. Simplified Structure for Easy Maintenance
The overall structure is centered around a single screw, with fewer components. The disassembly and cleaning processes for the screw and barrel are simple, and routine maintenance does not require complex tools or specialized technical skills. Small and medium-sized manufacturers can complete maintenance with basic technicians, reducing downtime costs for equipment repairs. This is particularly suitable for scenarios with tight production schedules.
2. Low operational barriers and ease of use
Process parameters (temperature, speed) are adjusted through intuitive logic, eliminating the need for complex programming or multi-system coordination. New employees can master core operations after short-term training. When switching to simple products, only the mold needs to be replaced and parameters slightly adjusted, eliminating the need for material clearance or screw combination adjustments required by twin-screw extruders. This makes it suitable for flexible production of small batches and multiple varieties.
3. More controllable equipment and operating costs
The initial purchase cost is lower than that of twin-screw models, and due to its simple structure, the cost of replacing spare parts (such as screws and heating rings) is low. During operation, energy consumption is concentrated on barrel heating and screw drive, without additional energy consumption from complex transmission systems. This significantly reduces electricity costs and equipment depreciation pressure in long-term production, making it more suitable for cost-sensitive small and medium-sized enterprises.
4. Outstanding stability in continuous production
The uniform and continuous pushing force generated by screw rotation ensures stable material plasticization and extrusion speed. The resulting products, such as pipes and films, exhibit strong consistency in thickness and cross-sectional shape, making them suitable for standardized products with high requirements for uniform specifications (e.g., construction pipes, packaging films), thereby reducing scrap rates caused by parameter fluctuations.
5. Suitable for basic raw material processing needs
It has stable processing capabilities for granular virgin materials and simple crushed recycled materials, without the need for complex pre-mixing or degassing processes. Raw materials can be directly melted and extruded into shape. Even modified materials with small amounts of additives (such as color masterbatches or antioxidants) can meet basic dispersion requirements through the screw’s shear mixing, without relying on the strong mixing function of a twin-screw extruder.
Common Questions About Single-Screw Extruders
Q:What raw materials can be processed by a single-screw extruder?
A:Single-screw extruders primarily process general-purpose plastics such as PE, PP, and PVC pellets. They can also handle certain dry powders and simple recycled materials (e.g., clean plastic scrap). However, they have limited compatibility with complex modified materials like high-filler compounds or glass-fiber-reinforced materials, making uniform mixing difficult. They are better suited for processing raw materials with single or small amounts of additives.
Q:Disadvantages of single-screw extruders
A:Single-screw extruders have weak mixing capabilities, leading to uneven dispersion of multi-component raw materials; when processing high-viscosity or heat-sensitive materials, uneven plasticization can cause scorching; cleaning is cumbersome, with significant residual material during material changes; they have poor adaptability for complex modified or high-filler processes, making it difficult to meet the requirements for high-precision products.
Q:Differences between single-screw and twin-screw extruders
A:Single-screw extruders rely on a single screw to convey material, have weak mixing capabilities, and are suitable for simple raw materials and basic products; twin-screw extruders have two intermeshing screws, generate strong shear forces, can process complex and modified materials, achieve high mixing uniformity, but have complex structures, higher costs, and greater operational and maintenance difficulties.